Earthquakes are natural phenomena that can be extremely frightening for those who experience them. The mere sensation of the ground shaking beneath you often leads to a desperate wish for it to stop quickly. Such disasters result in extensive property damage and claim thousands of lives, alongside their subsequent effects on water bodies, leading to tsunamis that can make matters even worse. We frequently hear terrifying stories about earthquakes and their ability to devastate an area in the blink of an eye. Despite advancements in technology, controlling this phenomenon remains challenging. Statistics show that between 50 to 80 earthquakes occur daily, totaling about 2000 annually. Unfortunately, they occur suddenly without warning signs, unlike volcanoes, which contributes to high loss rates due to inadequate preparedness. Despite ongoing efforts by governments to educate the public about earthquake risks and preparedness, these efforts are still insufficient.
What Causes Earthquakes?
The Earth’s structure consists of layers, starting from the inner core, followed by the mantle made of molten magma, and finally the crust, which is composed of tectonic plates. These plates are known to move constantly due to thermal currents caused by molten magma. The tectonic plates in the oceans are called oceanic plates, while those on the continents are called continental plates. The movement of these plates leads to the formation of mountains and valleys, and they can interact with each other either by moving apart or coming together, causing one plate to slip under another. The point where they meet is called a fault line, which is where the Earth’s crust breaks. This results in the release of a massive amount of energy accumulated and stored during the movement of these plates, causing earthquakes felt by living beings, including humans. The severity of an earthquake depends on the amount of energy released from below.
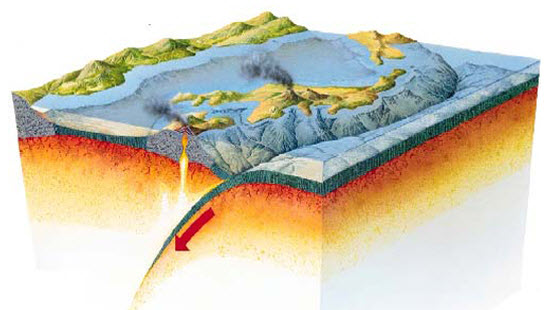
In rare cases, smaller tremors, known as foreshocks, may precede major earthquakes in the same area, referred to as the main shock. Scientists have not yet determined if these smaller tremors are reliable indicators of a larger quake. However, after a major earthquake, aftershocks—smaller quakes following the main shock—usually occur. Depending on the magnitude of the main shock, aftershocks can continue for weeks, months, or even years. Earthquakes occur when potential energy within tectonic plates is released from a focal point called the “epicenter,” usually located at shallow depths beneath the Earth’s surface, producing seismic waves that spread in all directions. The speed of these waves varies depending on the type of material they pass through, whether solid ground or water.
Types of Earthquakes
Earthquakes can be categorized into several types:
Tectonic Earthquakes
These are the most common type, resulting from the movement of tectonic plates. These plates move slowly and can slide past each other, move apart, or collide. When two moving plates slide past each other, a tectonic earthquake occurs, which can vary in magnitude from small to large. Tectonic earthquakes are responsible for most of the planet’s significant damage and can destroy entire cities in seconds if their magnitude is high enough.
Volcanic Earthquakes
Compared to tectonic earthquakes, volcanic earthquakes are less common. They usually occur before or after a volcanic eruption and come in two forms. The first type, tectonic volcanic earthquakes, happens after a volcanic eruption when magma erupts from the Earth’s crust, creating voids. Often, the magma fills these voids during volcanic activity, leading to high pressure and explosive eruptions, causing severe earthquakes. The second type, long-term volcanic earthquakes, occurs after a volcanic eruption. Changes in temperature within magma before an eruption lead to seismic waves, resulting in earthquakes.
Explosive Earthquakes
These result from nuclear explosions, representing the greatest impact of modern nuclear warfare. During nuclear tests conducted by the United States in the 1930s, many towns and villages were destroyed due to these explosions.
Collapse Earthquakes
These smaller earthquakes are commonly associated with underground mining activities and are sometimes referred to as “rockbursts.” They are caused by pressure build-up within rocks, leading to the collapse of mine roofs and subsequent smaller tremors. Such earthquakes are prevalent in small towns with underground mines.
The Devastating Effects of Earthquakes

Earthquakes have many destructive effects on property and lives, causing economic losses running into billions of dollars. They can be summarized as follows:
Building Collapse
Severe earthquakes can cause buildings to collapse entirely. The resulting debris poses a significant risk as falling objects can be fatal. Earthquakes also shatter mirrors and windows, further endangering lives.
Infrastructure Damage
Earthquakes can knock down power lines, which is dangerous due to the risk of electrocution or fires caused by exposed wires. They can also destroy roads, water pipelines, and gas lines, leading to leaks that might cause explosions and uncontrollable fires.
Landslides and Rockfalls
Earthquakes can displace large rocks and land sections on slopes, causing them to tumble rapidly downwards. This can result in devastation and death for people living in the valleys below.
Flooding
Strong earthquakes can crack dam walls, leading to either immediate or gradual failures, which can send torrents of water to nearby areas, causing massive floods.
Tsunamis
Tsunamis are long series of ocean waves caused by underwater earthquakes or volcanic eruptions. They can devastate coastal communities, as seen on March 11, 2011, when a tsunami struck Japan, resulting in over 18,000 deaths.

Liquefaction
Liquefaction occurs when saturated soil loses its strength and behaves like a liquid. Buildings and other structures on such soil can sink or topple. Earthquakes are responsible for most liquefaction events worldwide, such as the 1692 disaster in Jamaica that destroyed Port Royal.
How Are Earthquakes Measured?
Earthquakes are measured based on the amount of energy they produce using the Richter scale, developed by Charles Richter of the California Institute of Technology. The Richter scale uses data from measuring the energy released to determine the earthquake’s magnitude. Earthquakes above 7 on the Richter scale are considered destructive and can cause severe damage to lives and property. Another device called a seismograph measures and records seismic vibrations and ground movements.

Generally, earthquakes below 3 on the Richter scale are not felt. Earthquakes between 3 and 6 are considered minor, with countries like Japan frequently experiencing them due to their seismically active location. When an earthquake occurs underwater, it can trigger tsunamis, such as the devastating one in the Indian Ocean on December 26, 2004.
Can Earthquakes Be Predicted?
Currently, predicting earthquakes remains elusive. Despite technological advancements and various methods, none have been successful in forecasting earthquakes. However, efforts continue, as successful prediction could save many lives in the future. Meanwhile, what can be done is to educate yourself on how to respond during an earthquake and take precautionary measures, such as avoiding properties in known seismic zones or fault lines.
