South Korea is a country located in East Asia, situated on the southern part of the Korean Peninsula. It is recognized as one of the leading global economic and technological powers.
Geography
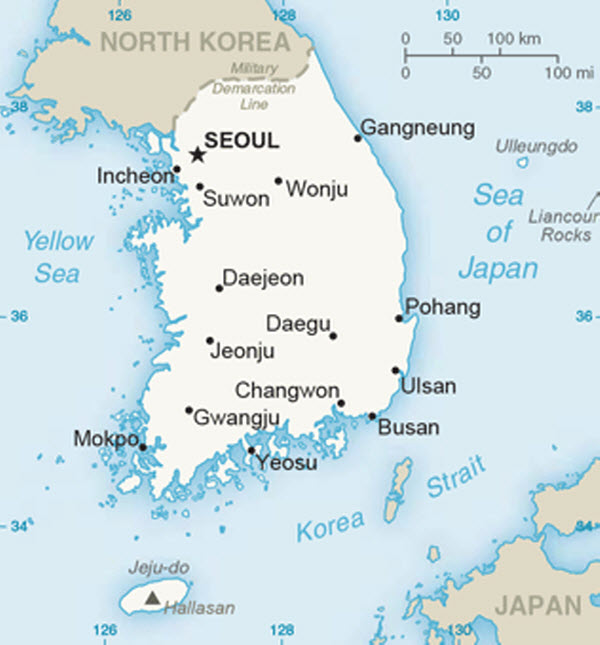
Location: East Asia, Southern Korean Peninsula
Coordinates: Approximately 35.9078° N, 127.7669° E
Area: About 100,363 square kilometers, consisting of the mainland and over 3,000 islands.
Borders:
- North: North Korea (about 238 kilometers)
- East: Sea of Japan (East Sea)
- West: Yellow Sea
- South: Korea Strait, which separates it from Japan
Climate:
- Temperate climate with four distinct seasons: cold winters, warm and humid summers, pleasant spring and autumn.
Topography:
- Includes mostly mountainous terrain with lowlands along the western and southern coasts. Significant rivers include the Han River and the Nakdong River.
Elevation:
- The highest peak is Hallasan, a volcanic mountain on Jeju Island, with an elevation of 1,947 meters.
Natural Resources:
- Limited natural resources include coal, tungsten, graphite, molybdenum, and small deposits of iron ore and copper.
Land Use:
- 19% agriculture, 64% forests, 17% built-up areas and other uses.
Population Distribution:
- Population is highly concentrated in urban areas, especially in the capital Seoul, as well as Busan, Incheon, and Daegu.
Population and Society

Population: Approximately 51.7 million (2024 estimate).
Ethnic Groups:
- Predominantly ethnically homogeneous, with 96% of the population being Korean. Small numbers of Chinese, Vietnamese, and other immigrants.
Languages:
- Korean is the official language. English is widely taught and used in business and education.
Religions:
- Christianity (about 28%), Buddhism (15%), and a significant portion of the population is unaffiliated or practices traditional beliefs.
Age Structure:
- Includes a growing elderly population with a rapidly aging society and a declining birth rate.
Population Growth Rate:
- Population is nearly stable with a very low growth rate (0.1%).
Country

Country Name: Republic of Korea (ROK)
Common Name: South Korea
Reason for Name: Reflects the country’s location on the southern half of the Korean Peninsula.
Type of Government: Presidential Republic.
Capital: Seoul
Reason for Naming Capital: Seoul is a historic and modern political, cultural, and economic hub of Korea.
Local Time: Korea Standard Time (KST), UTC+9, no daylight saving time.
Administrative Divisions: 9 provinces and 7 metropolitan cities.
Independence: Declared independence from Japan on August 15, 1945, and officially established on August 15, 1948.
Citizenship Acquisition: Through birth in Korea, legal residency, or naturalization.
Legal System: Civil law system based on the Constitution of South Korea.
Executive Branch: The President is the head of state and government.
Legislative Branch: Unicameral National Assembly.
Judicial Branch: The Constitutional Court and the Supreme Court of Korea.
Political Parties: Democratic Party of Korea, People Power Party, and others.
Flag Description: The flag is white with a red and blue “taegeuk” symbol in the center, surrounded by four black trigrams, one in each corner, representing harmony, balance, and the principles of yin and yang.
Country Code: KOR
Economy
GDP: Approximately $2.1 trillion USD.
Agricultural and Animal Products: Rice, barley, vegetables, fruit, livestock products.
Industries: Includes electronics, automobiles, shipbuilding, steel, chemicals, and telecommunications.
Budget: Surplus/deficit fluctuates based on economic conditions.
Exports: Semiconductors, automobiles, petrochemicals, ships, and electronics.
Imports: Oil, raw materials, machinery, chemicals, food products.
Foreign Reserves: Approximately $400 billion USD.
External Debt: About $600 billion USD.
Local Currency: South Korean Won (KRW).
Communications
Landlines: About 14 million lines.
Mobile Lines: About 70 million lines.
Country Code: +82
Broadcast Media: Includes several national and regional television and radio networks, with widespread internet access.
Internet Code: .kr
Internet Users: Approximately 49 million people.
Transportation

National Air Transport System: Highly developed network of airports and airlines.
Airports: About 28 airports, with Incheon International Airport being a major hub.
Helipads: Numerous, especially in urban areas.
Pipelines: Pipelines for oil, gas, and water distribution.
Railroads: Extensive railroad network including the KTX high-speed train system, with over 4,000 kilometers of track.
Road Network: Over 100,000 kilometers of well-maintained roads, including expressways.
Ports: Major ports include Busan, Incheon, and Gwangyang.
Military

Military Composition: Includes the Army, Navy, Air Force, and Marine Corps.
Military Spending: Approximately $45 billion USD annually.
Military and Security Personnel: About 600,000 active-duty personnel.
Military Equipment: Includes advanced fighter jets, naval vessels, tanks, and missile systems.
Military Service Age: Mandatory military service for males, aged 18 to 28, for about 18 to 21 months depending on the branch.
